Each year, water insecurity costs the global economy $500 billion
Source: Report of the GWP/OECD Task Force on Water Security and Sustainable Growth
What is Integrated Drought Management?
Integrated Drought Management mitigates drought risk and builds drought resilience by addressing multiple components of drought management, including disaster risk reduction, climate adaptation strategies and national water policies. Integrated Drought Management accounts for the needs of all stakeholders affected by drought. In 2013, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the Global Water Partnership (GWP) launched the Integrated Drought Management Programme (IDMP) to address drought issues more effectively. IDMP provides advice and guidelines to communities, countries and regions affected by drought through the Integrated Drought Management HelpDesk.
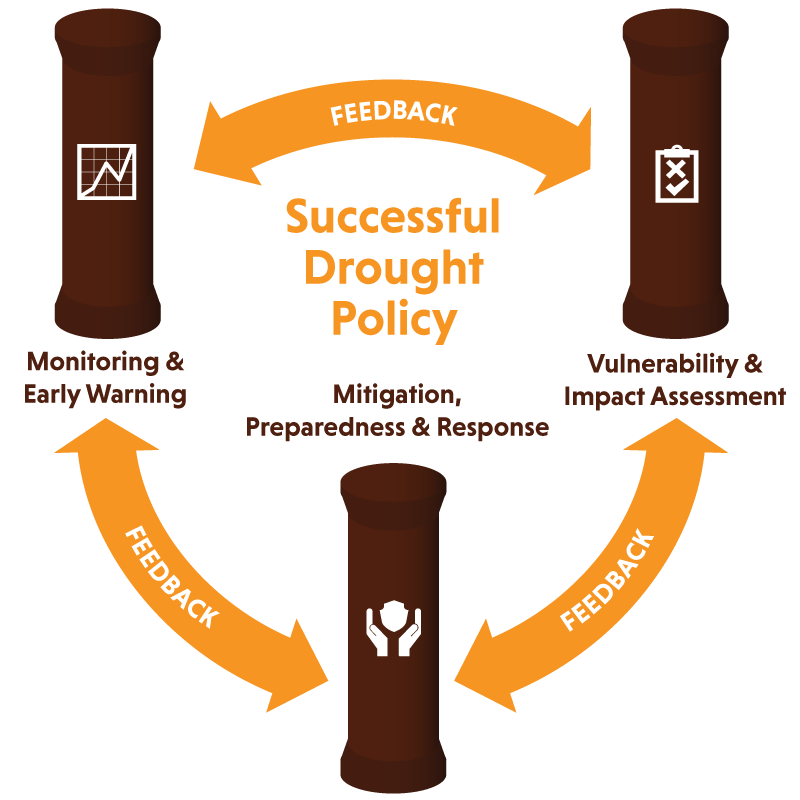
The Three Pillars of Drought Management
#1 Monitoring and Early Warning Systems: It is critical to monitor drought indicators such as precipitation, temperature, soil moisture, vegetation, streamflow and ground water. Early warning systems analyze these drought indicators and disseminate drought forecasts to key stakeholders in a timely manner.
#2 Vulnerability and Impact Assessment: A vulnerability and impact assessment considers social, economic and environmental factors to determine a community’s susceptibility to drought hazards. For example, women, children, pastoralists, farmers and marginalized communities could be vulnerable population groups.
#3 Mitigation and Response: Drought mitigation includes both the structural (i.e. appropriate crops, dams and engineering projects) and non-structural measures (i.e. policies, public awareness, and legal framework) necessary to limit the adverse impacts of drought. Drought response refers to the assistance administered during or immediately after the drought to save lives and meet the affected community’s basic needs.
Citation: Capacity Development to Support National Drought Management Policies

About the Integrated Drought Management Programme (IDMP)
IDMP’s objective is to support stakeholders at all levels by providing policy and management guidance and by sharing scientific information, knowledge and best practices for Integrated Drought Management.
IDMP’s Approach:
1. Shift focus from reactive to proactive
2. Foster horizontal integration by collaborating with partners from diverse sectors
3. Facilitate vertical integration on global, regional, national and local levels
4. Improve knowledge base with better access to information
5. Promote projects that demonstrate innovation
6. Build countries’ capacity to implement integrated approaches
About
Core Documents
Contact
For further information please contact the IDMP Technical Support Unit at: droughtmanagement@wmo.int
Meet IDMP’s Co-sponsors:

The Global Water Partnership (GWP) is a global action network with over 3,000 partner organizations in 183 countries. The network has 86 Country Water Partnerships and 13 Regional Water Partnerships.
The network is open to all organizations involved in water resources management: developed and developing country government institutions, agencies of the United Nations, bi- and multilateral development banks, professional associations, research institutions, non-governmental organizations, and the private sector.
GWP’s action network provides knowledge and builds capacity to improve water management at all levels: global, national and local. GWP does not operate alone. Its networking approach provides a mechanism for coordinated action and adds value to the work of many other key development partners.

The World Meteorological Organization (WMO), founded in 1950, is a specialized agency of the United Nations for weather, climate and water. WMO is dedicated to international cooperation and coordination on the state and behavior of the Earth’s atmosphere, its interaction with the land and oceans, the weather and climate it produces, and the resulting distribution of water resources.
Through its Technical Commission, Programmes and Regional Offices as well as by synergistic partnerships, WMO facilitates the maintenance and expansion of its Members’ atmospheric, oceanographic and land-based observational networks; the free unrestricted exchange of the resulting data and information; and related capacity development and research in order to optimize the production of weather, climate and water-related services worldwide.


